NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) have catalyzed a revolution in the world of digital assets, offering unique opportunities to artists, collectors, and investors. However, to fully grasp their value and uniqueness, it is essential to delve into their internal mechanisms. This article will provide you with an in-depth analysis of how NFTs work, exploring the fundamentals of blockchain, smart contracts, and the significance of metadata.
How NFTs Work from a Technical Perspective?
Understanding the inner workings of NFTs is the key to successful immersion in the world of digital assets. Thanks to blockchain, smart contracts, and metadata, NFTs evolve beyond mere technological advancements, transforming into art, investment opportunities, and unique experiences for every participant in this captivating realm.
Here’s a brief overview of how NFTs function from a technical standpoint:
- Blockchain: This serves as the foundation upon which NFTs are built. It ensures the uniqueness of each token, creating a secure chain of blocks to store information about ownership and origin.
- Smart Contracts: These are programs that automate NFT exchange processes. They guarantee the uniqueness of each token and oversee its transfer from one owner to another.
- Metadata: A pivotal component of every NFT, metadata contains information about the artist, origin, owner, and other crucial details. Metadata renders each token unique and valuable to collectors.
- Metadata Storage: Specialized servers or decentralized networks store NFT metadata. They ensure the security and accessibility of information about each token.
Now, let’s delve into each point in more detail.
How NFTs Interact with Blockchain?
Non-Fungible Tokens are intricately intertwined with blockchain technology, giving birth to unique digital assets that can be identified, verified, and appreciated in both the art and cryptocurrency worlds. Today, there are several blockchains applicable for NFT operations, among which the most prominent ones include:
Their interaction ensures the transparency, security, and uniqueness of each token, making them valuable assets for collectors, investors, and artists alike. Thanks to blockchain technology, every NFT possesses a public ownership history. This means that every transaction associated with an NFT is tracked and recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and proof of ownership.
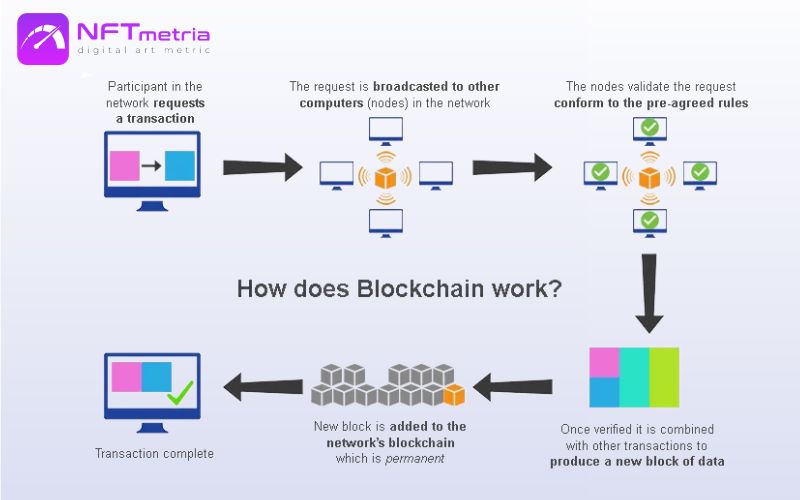
But how exactly do NFTs interact with blockchain, and how does this affect their uniqueness and value? Let’s delve into the details:
- Uniqueness and Blockchain: Each NFT is stored in the blockchain as a unique token. Blockchain serves as the foundation to confirm the uniqueness of each token, providing a distinctive digital fingerprint that is impossible to counterfeit. This confidence in the authenticity of each NFT gives them their fundamental value.
- Smart Contracts and NFTs: Smart contracts are pieces of code operating within the blockchain, defining the rules of creating, storing, and transferring NFTs. They automate processes related to NFTs, ensuring secure and transparent transactions. These smart contracts guarantee proper management and transfer of NFTs between owners.
- Metadata and Identity: Metadata associated with each NFT contains information about its origin, owner, and history. This data is stored in the blockchain, ensuring the identity and history of each token. Metadata renders each NFT unique and adds to its value.
- Decentralized Storage: Blockchain typically employs decentralized storage systems for NFT metadata. This means that information about each token is distributed across multiple nodes in the network, ensuring data security and resilience. Decentralized storage prevents data loss and preserves the value of each NFT.
The integration of NFTs with blockchain technology not only ensures their authenticity but also adds layers of value and trust, making them highly coveted assets in the digital landscape.
How are NFTs connected with smart contracts?
NFTs operate using smart contracts in the blockchain. Here’s how it works:
- Creating Uniqueness: Initially, a smart contract defines parameters that make the NFT unique, such as its metadata, including images, videos, music, and other characteristics. These parameters are assigned to each NFT, making it distinct from other tokens.
- Blockchain Registration: Once the NFT is created, the smart contract registers it in the blockchain, assigning a unique identifier (for example, a token ID). This identifier is used for the unequivocal identification of each token in the network.
- Ownership and Transfer Management: The smart contract also manages the transfer and ownership of the NFT. It defines conditions under which the token can be transferred from one owner to another. This ensures secure and transparent transactions.
- Programming Additional Functions: Smart contracts can be configured to include additional functions, such as royalties for the NFT creator with each subsequent sale. When the NFT is resold, the smart contract automatically distributes royalties between the previous owner and the creator.
- Confirming Authenticity and Uniqueness: The smart contract verifies the authenticity and uniqueness of the NFT. This provides trust and security to the owners, convincing them of the uniqueness and originality of their digital asset.
In conclusion, smart contracts serve as the foundation for creating, managing, and trading NFTs, ensuring transparency, reliability, and uniqueness in the world of digital assets.
Types of Smart Contracts for NFTs
Non-Fungible Tokens utilize various types of smart contracts, each serving specific purposes and functions. Here are some of the most common types of smart contracts for NFTs:
- ERC-721 Standard: This standard is the most prevalent for creating NFTs on the Ethereum blockchain. Each token generated using ERC-721 is unique and non-fungible, making it ideal for creating collectibles, trading cards, music, sport, membership, utility tokens , art, and other unique assets.
- ERC-1155 Standard: This standard supports both unique and fungible tokens within the same contract. It allows the creation of not only unique NFTs but also tokens that are interchangeable and identical to each other. This versatility makes ERC-1155 a more flexible option for various applications, such as games and virtual worlds.
While there are other standards/types of smart contracts for NFTs, the two mentioned above have gained recognition and applicability in the market today. Each of these standards provides unique features and capabilities for creating and managing NFTs, making them suitable for various use cases in the world of decentralized applications, art, and gaming.
How NFTs Interact with Metadata and Data Storage?
Non-Fungible Tokens are closely linked with metadata and data storage in terms of their uniqueness and value. Here’s how these components interact:
- Metadata:
- Description and Uniqueness: NFT metadata contains information about the item it represents. This can include token description, author name, creation date, and other characteristics that make each token unique.
- Digital Content: Metadata can also include links to digital content, such as images, videos, music, or other files associated with the token. These files are typically stored in decentralized storage systems.
- Data Storage:
- Decentralized Storage: Digital content linked in metadata is often stored in decentralized data storage systems like IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) or Arweave. These systems ensure long-term and secure file storage, accessed through hash links provided in the metadata.
- Resilience and Security: Decentralized storage ensures data resilience, as files are stored across multiple nodes in the network. This also enhances security, as data isn’t reliant on a single centralized source.
When NFTs are created, their metadata, including links to digital content, is recorded in a smart contract on the blockchain. Metadata can indicate the data storage location where the actual files reside. This ensures transparency and long-term accessibility to the content of NFTs.
Through this approach, NFTs become unique and valuable digital assets. Owners can be confident in the uniqueness and distinctiveness of their digital collections.
Conclusion
In our immersion into the world of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), we have unveiled the mysteries of their inner workings. From blockchain technologies to metadata and smart contracts, we delved into every layer that makes NFTs unique and captivating.
These technologies, akin to magic, breathe life into digital assets, imbuing them with distinctiveness and value. Thanks to metadata, each token becomes a unique work of art, a valuable historical artifact in the virtual realm. Smart contracts provide reliability and security, while the blockchain records every transaction, rendering NFTs transparent and authentic.
So, are you ready to dive into the world of NFTs? Before you stretches a digital landscape full of possibilities and discoveries. Fear not to explore, create, invest, and collect – because each NFT carries not only value and investment appeal but also a unique story. Know that, armed with your knowledge and broad perspective in the NFT market, you can successfully profit from NFTs. Go ahead boldly, and may your journey in the world of NFTs be both captivating and inspiring!